7 April 2025


What Is Green Methanol?
Green methanol (also referred to as e-methanol) is a liquid chemical compound produced using renewable energy, green hydrogen, and captured carbon dioxide (CO₂). Unlike conventional methanol, which is derived from fossil fuels like natural gas or coal, green methanol is produced sustainably and can achieve near-zero carbon emissions over its lifecycle.
How Is Green Methanol Produced?
1. Renewable Electricity Generation Green methanol production begins with generating electricity from renewable sources such as wind, solar, or hydropower. This electricity powers the electrolysis process.
IEA: Renewables 2023 - https://www.iea.org/reports/renewables-2023
2. Electrolysis for Green Hydrogen An electrolyser uses this clean electricity to split water into hydrogen and oxygen. The hydrogen (H₂) is captured for methanol synthesis, while oxygen is released back into the atmosphere.
IRENA: Green Hydrogen - https://www.irena.org/hydrogen
3. Carbon Dioxide Capture The CO₂ needed for synthesis is captured from sustainable sources, such as biomass power plants, where emissions are part of the natural carbon cycle rather than from fossil combustion.
IEA: CO₂ Capture, Utilisation and Storage - https://www.iea.org/topics/carbon-capture-utilisation-and-storage
4. Methanol Synthesis Hydrogen and carbon dioxide are combined in a synthesis reactor, creating methanol (CH₃OH) through a catalytic reaction. This methanol is then distilled to remove impurities.
ScienceDirect https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S036031991934317X
5. Storage and Transport One of green methanol’s key advantages is its liquid state at ambient conditions, making it easy to store, transport, and integrate with existing fuel infrastructure.
Methanol Institute - https://www.methanol.org/
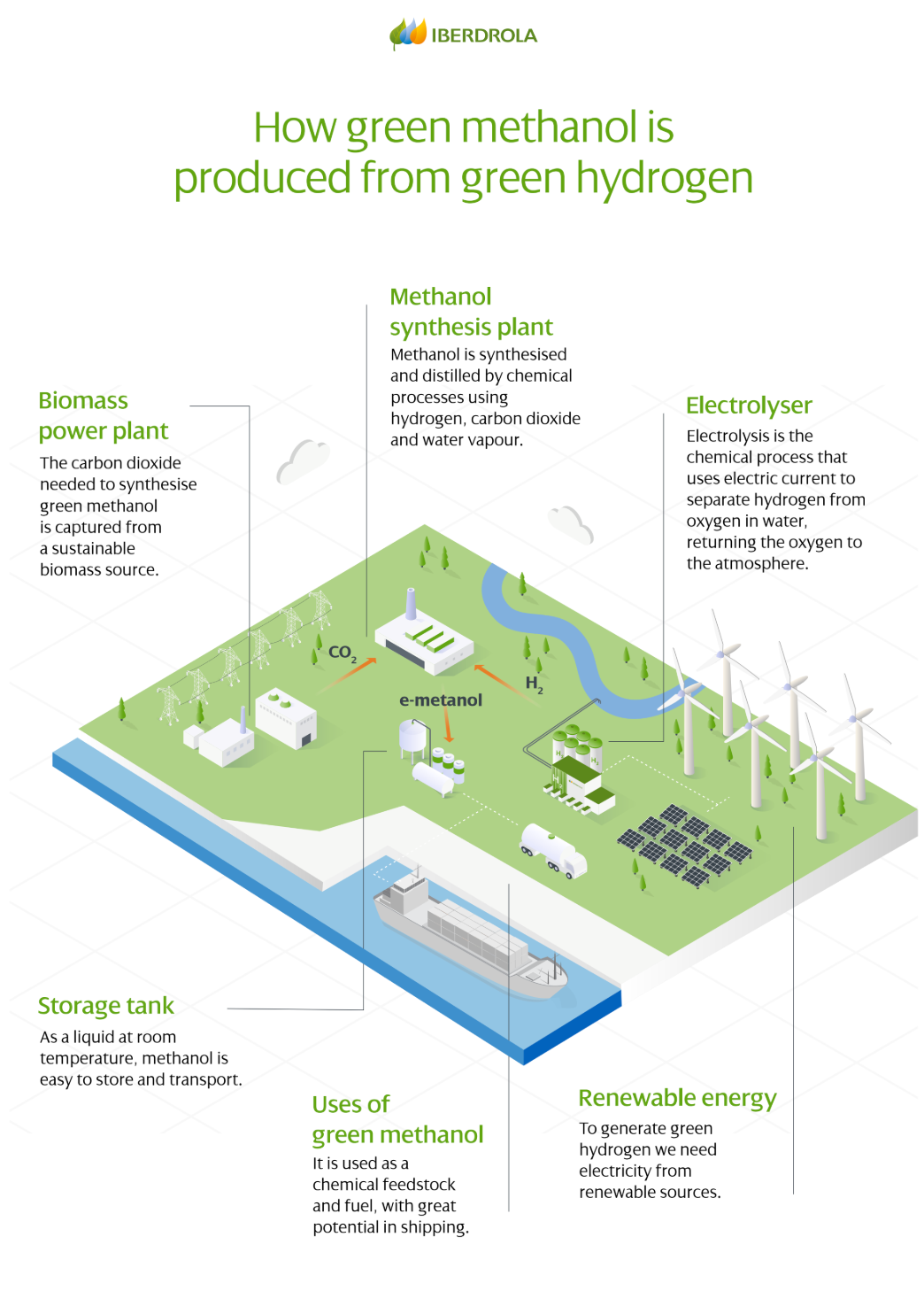
Applications and Market Potential
Maersk - https://www.maersk.com/news/articles/2023/06/20/a-landmark-day-for-green-methanol
Chemical Industry: As a feedstock, green methanol can be used to produce plastics, adhesives, paints, and other everyday materials—without the fossil fuel footprint.
Energy Storage: It can also serve as a form of chemical energy storage, converting excess renewable electricity into a storable liquid fuel.
Environmental Benefits
Air Quality: It produces lower emissions of sulfur oxides (SOx), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulates compared to diesel or bunker fuel.
Biodiversity: Reducing dependency on fossil fuels helps mitigate climate change, indirectly protecting ecosystems.
Challenges and Outlook
Green methanol’s scalability depends on several factors:
- Availability of low-cost renewable electricity.
- Development of carbon capture infrastructure.
- Policy incentives and regulatory frameworks to make it cost-competitive.
Still, with growing global momentum toward green shipping, hydrogen economies, and net- zero goals, green methanol stands out as a promising solution.
Conclusion
For tailored insights or technical consulting in clean energy transitions and low-carbon infrastructure, contact our team.

Come work with Us!
If you cannot carry out new cases in your current firms due to conflicts of interest, come work with us!
- Modern case management platforms
- Unrivalled team and admin support
- Clear and concise quality management systems
- Exceptional reputation
- Capacity to GROW
- Remote working
DAC is the future of working as an Expert Witness.

79a Grapes House
Suite 4
First Floor Esher
Greater London
United Kingdom
KT10 9QA










































